Putting the Judiciary in Its Place

January 22, 1973 (Roe vs Wade) was a glaring act of social engineering by an unconstitutional judiciary. "We the people" are the first three words of the Constitution, but since the 1940s, American government has been dominated by, "We the judges." Sanctity of human life, Bible reading and prayer in public schools, the display of the Ten Commandments, Christmas nativities, same-sex marriage, and a host of additional social, religious, and moral issues have been decided, not by "We the people," but by "we the judges." Putting the Judiciary in Its Place
 The United States Constitution does not provide for three equal branches of government. The judiciary was intentionally made the weakest of all three branches.
The United States Constitution does not provide for three equal branches of government. The judiciary was intentionally made the weakest of all three branches.Throughout the twentieth century, the judiciary has accrued powers for itself that America's Founding Fathers never intended. The Declaration of Independence, listed four abuses (complaints 8, 9, 15, and 18) that were associated with the King's courts and judges. In the Constitution, the Founding Fathers corrected those abuses. Putting the Judiciary in Its Place
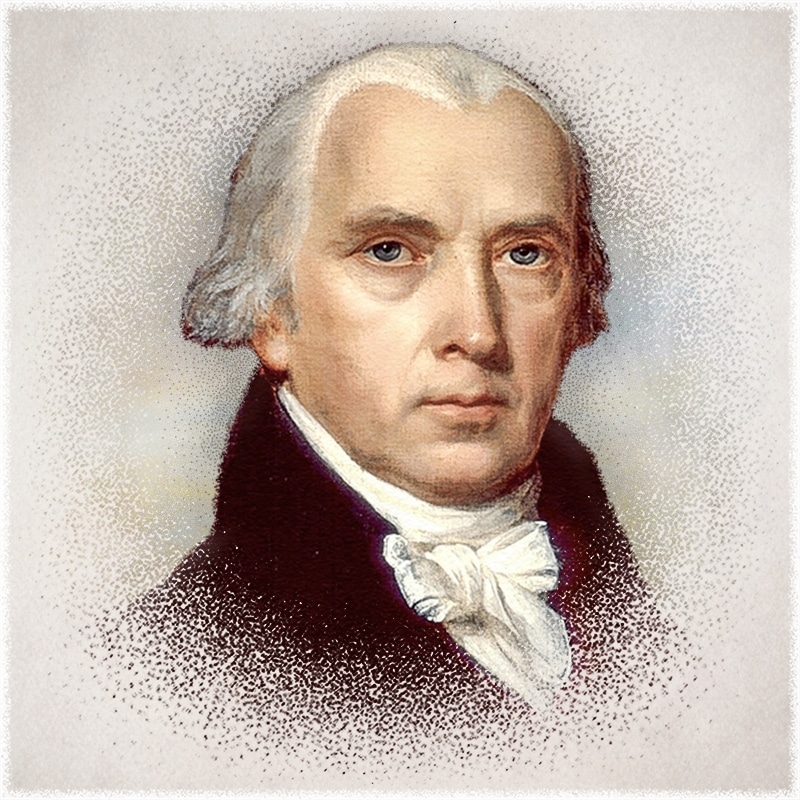
Despite the fact America's Founding Fathers did not intend that there be three equal branches of government, the judiciary has demanded—not only a place of equality—but a place of supremacy, and the legislative and executive branches have bowed to that demand. The Federalist Papers—written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and America's first Chief Justice, John Jay—were a means used to convince fledgling America to vote in favor of the Constitution. In Federalist Paper #78, James Madison—the alleged "Architect of the Constitution"—articulated the prevailing philosophy concerning the place of the judiciary in American government when he wrote:
It proves incontestably that the judiciary is beyond comparison the weakest of the three departments of power; that it can never attack with success either of the other two…It equally proves that though individual oppression may now and then proceed from the courts of justice, the general liberty of the people can never be endangered from that quarter...[1]
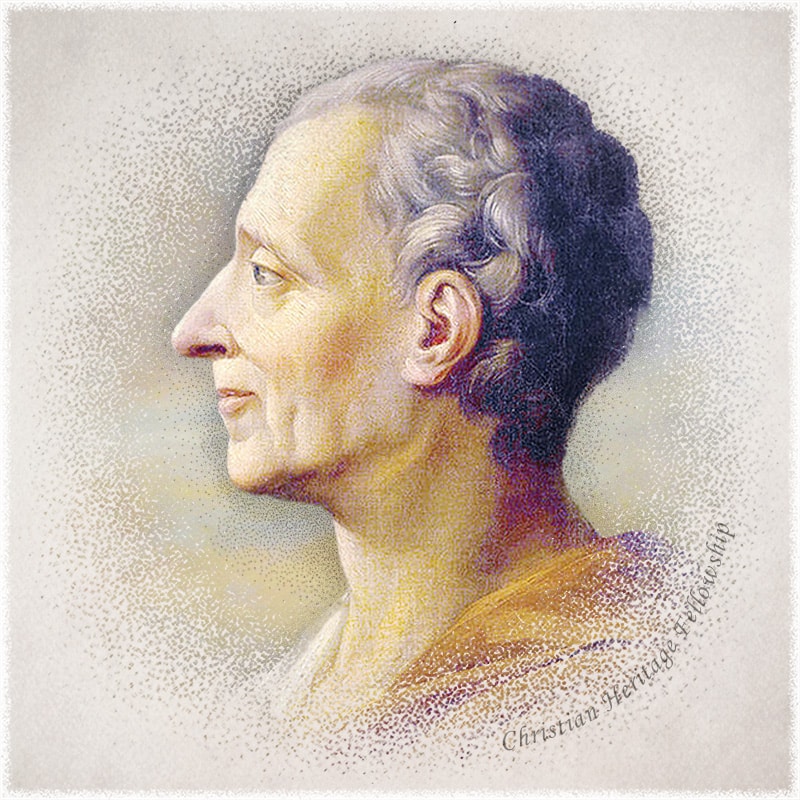
Charles Hyneman was Distinguished Professor of Political Science at Indiana University. Together with Donald S. Lutz, Professor of Political Science at the University of Huston, these two professors reviewed an estimated 15,000 political documents from the founding era of America as an independent nation—an era of nearly half a century, extending from 1760 to 1805. Hyneman and Lutz deduced from their extensive study that the single most sited source in the writings of America's Founding Fathers was the Bible with 34% of the quotes.[2] The second most frequently sited source was French political philosopher, Baron Charles Montesquieu who ranked a distant second with 8.3% of the total quotes. After discussing the differences between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government in the first volume of The Spirit of the Law, Montesquieu vividly concluded:
Of the three powers above mentioned, the judiciary is in some measure next to nothing...[3]
Such was the understanding of Baron Montesquieu—the second most important influence upon the political thought of America's Founders.
What is significant is that the most important work used in support of the ratification of the Constitution did not give the judiciary or the courts equal standing with the other branches of government. They recognized that King George's judges had abused their power, and the judiciary was the easiest means for a judge or branch to accrue power for itself.
It was universally understood by the Founding Fathers that the judiciary should always occupy a lesser role than the legislative and executive branches. A survey of the Constitution itself clearly demonstrates that "We the people" or legislative branch was to exercise most of the duties of government. After the legislative branch, the executive branch bears lesser authority, and the branch given the least amount authority by the Constitution is the judiciary.
For this reason, the Founding Fathers gave the judiciary no place of prominence. The legislative and executive branches were given buildings to exercise their responsibilities, but the Supreme Court had no home until 1935. Prior to this, the Court bounced around in the Capitol, finding a place to hear cases wherever space was available. In addition, the Constitution made the judiciary toothless—giving it no power to act on its own
The Founders did not believe the judiciary had Constitutional authority to nullify the work of the legislative or executive branches—something far different than the current deference rendered to the courts. In the case of Marbury vs Madison (1803), Jefferson nullified the decision of Chief Justice John Marshall and the Supreme Court. And, Republican Abraham Lincoln rejected the decision of the Democratic-controlled Supreme Court in Dred Scott vs Sandford (1857). These are only two instances among others when the judiciary was put in its place.
From abortion, to same-sex marriage, and well beyond, the judiciary has been permitted to terrorize America's morality and national life. America desperately needs legislators, governors, and presidents who will put the judiciary in its place! Give us men and women who have the courage of Jefferson, Lincoln, and others who have reminded the judiciary of its subordinate constitutional role!
[1] Also see Federalist Paper #51. Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, The Federalist Papers (New York: The Colonial press, 1901), 498.
[2] Donald S. Lutz, The Origin of American Constitutionalism (Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1988), 139-147.
[3] Baron De Montesquieu, The Spirit of Laws, trans. Thomas Nugent, Revised ed., 2 vols. (New York: The Colonial Press, 1899), 1:156.